Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to the most common questions about our materials, lead times, and ordering process.
What materials are available?
We print with industrial-grade materials including PLA, PETG, ABS, ASA, TPU, and PA12 — covering everything from simple prototypes to functional, high-strength components.
How do I get a quote?
Shoot us a message at [email protected] or use the contact form below. Attach your STL, STEP, or OBJ files and we’ll get back to you with pricing and lead time within 24 hours.
Do you offer bulk or production discounts?
Yes, we provide scaled pricing for batch runs, recurring orders, and long-term clients. Just mention your quantity when requesting a quote.
Where do you ship from?
All parts are produced and shipped directly from Schleswig, Germany. We deliver across the World with reliable, tracked shipping.
What’s your typical turnaround time?
Most orders are completed and shipped within 1–3 business days, depending on size and complexity. Larger production runs are scheduled individually.
Can I request custom materials or colors?
Absolutely, if you need a specific filament or color, we can order it in for your project. Just let us know in your quote request.
What tolerances can I expect?
Our FDM prints maintain ±0.2 mm dimensional accuracy, depending on part geometry and material. If you need tighter tolerances, just include that note in your quote request.
Do you offer resin or CNC machining?
Not yet, we currently focus entirely on FDM production to guarantee top reliability and speed. CNC and resin capabilities are planned for future expansion.
Can you help me improve my design before printing?
Yes. Every file is manually reviewed before printing, and we’ll reach out if we spot issues or ways to improve strength, fit, or surface finish. We don’t just print, we make sure your part works.
Turn your CAD files into real parts
Upload your files and get a fast, accurate quote for manufacturing. No back and forth. We review your design and handle production from start to finish.
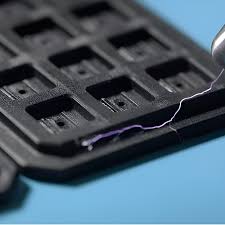
Why ESD-Safe 3D Printing Materials Matter and When You Actually Need Them
Most people don’t think about static electricity until something stops working. In electronics manufacturing, static discharge is one of the fastest ways to silently destroy components. And the worst part is that it often leaves no visible damage. The part looks fine. The device fails later.
Standard plastics are insulators. They store electrical charge. That makes normal 3D printed parts dangerous around sensitive electronics, PCBs, sensors, and semiconductors. This is where ESD-safe 3D printing materials come in.
They are not marketing hype. They solve a real industrial problem.
What is ESD and why does it matter?
Electrostatic discharge happens when two materials exchange electrical charge and that charge suddenly releases. In electronics, that discharge can be enough to destroy microchips, weaken components, or reduce product lifespan without immediate failure.
If you are working with:
PCBs
Sensors
Microcontrollers
Robotics electronics
Test fixtures
Then static is already part of your risk profile.
What makes ESD-safe materials different
Normal plastics like PLA, PETG, ABS, and Nylon are electrical insulators. They allow charge to build up.
ESD-safe plastics are engineered to slowly dissipate charge instead of storing it. They sit in a controlled middle zone between:
Insulators that trap charge
Conductors that dump charge instantly
This controlled dissipation protects sensitive components without creating new hazards.
How ESD 3D printing materials work
These materials contain conductive additives mixed into the plastic:
Carbon fibers
Carbon nanotubes
Conductive fillers
These additives form microscopic conductive paths through the material that allow static electricity to flow out safely.
The result is a plastic that still behaves mechanically like a polymer but electrically behaves in a controlled, predictable way.
Where ESD 3D printing is actually useful
This is not for decoration. This is for real industrial applications:
PCB holders and assembly fixtures
Electronics enclosures and housings
Static-safe tool organizers
Test rigs and measurement fixtures
Robotics end-of-arm tooling in electronics assembly
Cleanroom components
Part trays for sensitive components
Instead of buying expensive machined ESD tooling, you can print custom parts that fit your exact process.
When does ESD 3D printing make sense?
Use ESD materials if:
Your part touches electronics
Your part holds PCBs
Your part is used in electronics assembly
Your environment requires static control
Your tooling needs fast iteration
Do not use ESD materials if:
The part never interacts with electronics
Static discharge is not a concern
You only need decorative or structural parts
They cost more than standard filaments. Use them where they solve a real problem.
ESD vs normal plastic parts
Normal plastic:
Cheaper
Easier to print
Electrically unsafe for electronics
ESD plastic:
Slightly higher cost
More industrial printing requirements
Protects sensitive components
Enables professional manufacturing workflows
This is the difference between hobby printing and manufacturing printing.
Printing considerations
ESD materials are more abrasive than standard plastics. They usually require:
Hardened steel nozzles
Slightly slower print speeds
Proper drying and storage
Consistent quality control
That is the price of industrial reliability.
Why this matters for modern manufacturing:
Electronics are getting smaller, more sensitive, and more integrated into every product. At the same time, companies want faster development and lower tooling cost.
ESD-safe 3D printing sits exactly at that intersection:
Custom tooling
Low-volume production
Fast iteration
Static protection
It gives you manufacturing speed without sacrificing electronics safety.
If your workflow includes sensitive components, ignoring static protection is gambling with reliability.
We offer ESD-safe 3D printing for custom parts, fixtures, and enclosures.
Upload your file, choose your material, and get a real quote in minutes on this page: https://miloshevmachinery.com/quote





